

Multi-threaded computing
On the contrary to network computing, multi-threaded computing means multiple executions of a client program (or module) in a computer. The technology actually improves overall performance maximizing CPU usage. Modern computer OS (operating system) such as Microsoft Windows or Linux splits computer resources such as CPU and RAM and distributes the resource to each program for multi-tasking. Due to this reason, OS tends to reduce the performance of single software. For example, although Visual Gene Developer is busy calculating lots of functions, it doesn't use all CPU resources because Windows assigns one of threads (not exact but for a simple explanation) to single software and doesn't allow 100% occupation of the CPU process. To overcome the problem, multi-threaded computing technology was adopted to the software. Our software can execute additional clients on different threads and make use of all CPU and RAM resources as much as it can. Internally, although Visual Gene Developer utilizes a network computing module for multi-threaded computing, it works slightly differently from the network computing.
o Network connection
Because a server and clients don't interfere with each other, a user can use only a single server, only clients, or both of them. At the same time, clients can be connected to different servers using different IP address and port numbers. However, do not execute multiple Visual Gene Developer on a computer. Duplicate runs will cause software error due to duplicate accesses to a single thread.
1. Click on the 'Add Client' in the 'Network computing' menu.
You can see the first client window
Again click on the 'Add Client' in the 'Network computing' menu THREE TIMES.
In that way, you can make 4 active clients.
2. Input Host IP address and Port number
We assume that you are already executing Visual Gene Developer and activated a server on the same computer or on a remote computer
The IP address shown in the figure is a dynamic address. With regard to the dynamic IP address, check the 'Static vs. dynamic IP address' section below.
3. Click on the 'Connect' button
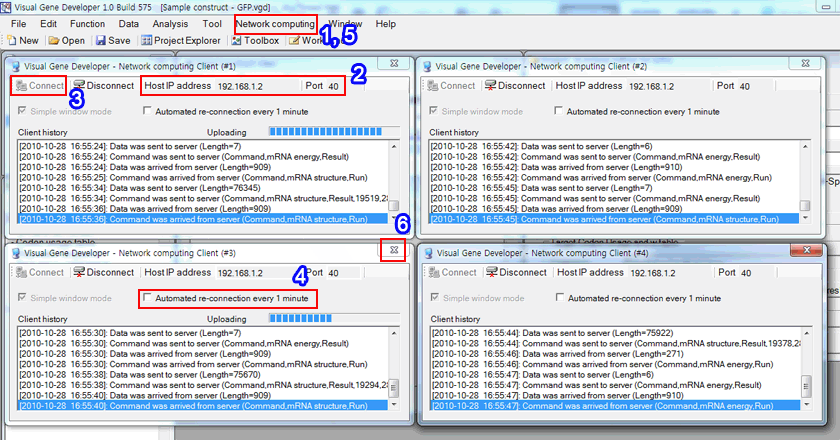
4. If you want to repeat connection every 1 minute, click on the 'Automated re-connection every 1-minute' button.
5. To remove clients, click on the 'Shutdown all clients' in the 'Network computing' menu
6. Or, click on the exit (X) button to deactivate a client one by one.
o NetComService class for module development
The software provides multi-threaded computing service at the class level. It helps users control network connections and develop new modules to utilize clients. For more details, check the 'Module development' section on the left menu.
o Static vs. dynamic IP address
In order to be connected to the server, clients need to know the server's IP address and port number. If you have static IP address (for example, a wire connected internet in a college) in a server computer, there is no problem regarding network connection. However, if your server IP address is dynamic (for example, internet connection provided by internet service companies) or are using wire/wireless routers, only local client computers that are connected to a router can be connected to a local server. However, it is not necessary for clients to have a static IP address. Only the server computer's IP address is important. Of course, there may be alternative ways to use a dynamic IP address for your server. Please search the web by yourself.
