

Gene optimization
Visual Gene Developer provides several algorithms to optimize gene constructs and find the best candidates.
Here is a summary of the implemented algorithms.
|
Module name |
Module category |
Description |
|
Monte-Carlo Codon Optimization |
Sequence optimization |
Predefined probability (defined in w-table file) based random mutation (=Monte-Carlo simulation). Target codons will be replaced by new codons that have a different probability. It checks following functions to screen out candidate gene constructs (Check CAI, Check restriction enzyme site, Check repeated sequence, Check excluded sequence) |
| Local mRNA Optimization | mRNA structure optimization | Adjust mRNA Gibbs energy to be in the specified range given by lowest Gibbs Energy (AvgBaseGibbs_Low) and highest Gibbs Energy (AvgBaseGibbs_High). It modified sequence performing Codon optimization or synonymous substitution. A user can set the target range given by Start and End locations in a sequence. |
| mRNA Profile Optimization | mRNA structure optimization |
Improved from Do_mRNAOpt_ProbabilityRandom. It optimizes an mRNA Gibbs energy profile along a long sequence. A moving window method was adopted. |
| Local mRNA Profile Optimization | mRNA structure optimization | Modification of Do_mRNAProfileOpt. A user can set the target range given by Start and End locations in a sequence. |
| Silent removal v1 |
Gene manipulation |
Remove undesired sequences. It can specify up to 10 sequences. |
| Silent removal v2 |
Gene manipulation |
Remove undesired sequences. Can process multiple query sequences. |
| Silent removal of potential polyadenylation sites |
Gene manipulation |
Remove predefined sequences of potential polyadenylation signal sequences |
|
Silent removal of potential intron cryptic splice sites |
Gene manipulation |
Remove predefined sequences of potential intron cryptic donor and receptor signal sequences |
|
Check CAI |
Constraint |
Return 'Not pass' if CAI value is lower than setpoint |
|
Check restriction enzyme site |
Constraint |
Return 'Not pass' if the sequence contains a certain restriction enzyme sequence |
|
Check repeated sequence |
Constraint |
Return 'Not pass' if the sequence contains a certain number of repeated sequence |
|
Check excluded sequence |
Constraint |
Return 'Not pass' if the sequence contains a certain excluded sequence |
|
Check stable mRNA structure |
Constraint |
Return 'Not pass' if the sequence contains stable mRNA secondary structures
The module retrieves sequence information and then generates lots of sequence segments specified by 'Window size'. The moving window scans along the sequence with a given 'Step size'. The Visual Gene Developer predicts mRNA secondary structure and calculates Gibbs free energy for each segment. If Gibbs energy is lower than a specified value ('Threshold value'), it returns 'Not pass' which means the gene includes stable mRNA secondary structure. If all sequence segments of the target gene are more unstable than the expected value ('Threshold value'), the module returns 'Pass'. |
For more details about the 'Module category', check the 'Module development' section on the left menu. At the same time, all predefined modules were summarized in the 'Class & module' section on the left menu.
Important!
Method 1 (Working on 'Workspace'): Paste sequence to 'Workspace' window and then click on the 'Function > Codon optimization'. You will see the 'Codon optimization' window. Adjust parameters and then click on the 'Perform' button. For mRNA structure optimization, click on the 'Function > mRNA optimization'. You will see the 'mRNA optimization' window. Adjust parameters and then click on the 'Analyze' button and then 'Optimize' button
Method 2 (Working on Gene construct): Firstly, configure optimization condition in the 'Configuration of gene optimization' window and then do optimize a gene construct in the 'Gene optimization' window.
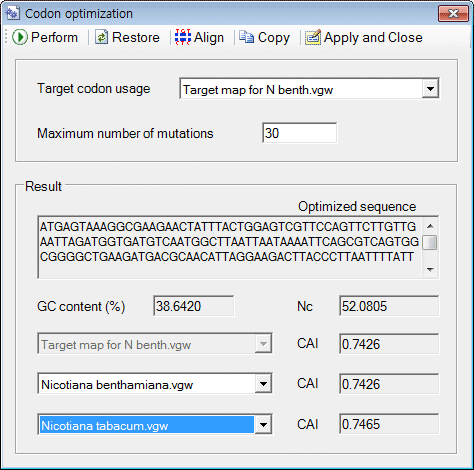
o Simply way to optimize codon on 'Codon optimization' window
1. Paste any sequence to the 'Workspace' window
2. Click on the menu item (Menu: Function > Codon optimization)
3. A window titled 'Codon optimization' will be shown.
4. Click on the 'Perform' button
5. Click on the 'Apply and Close' button
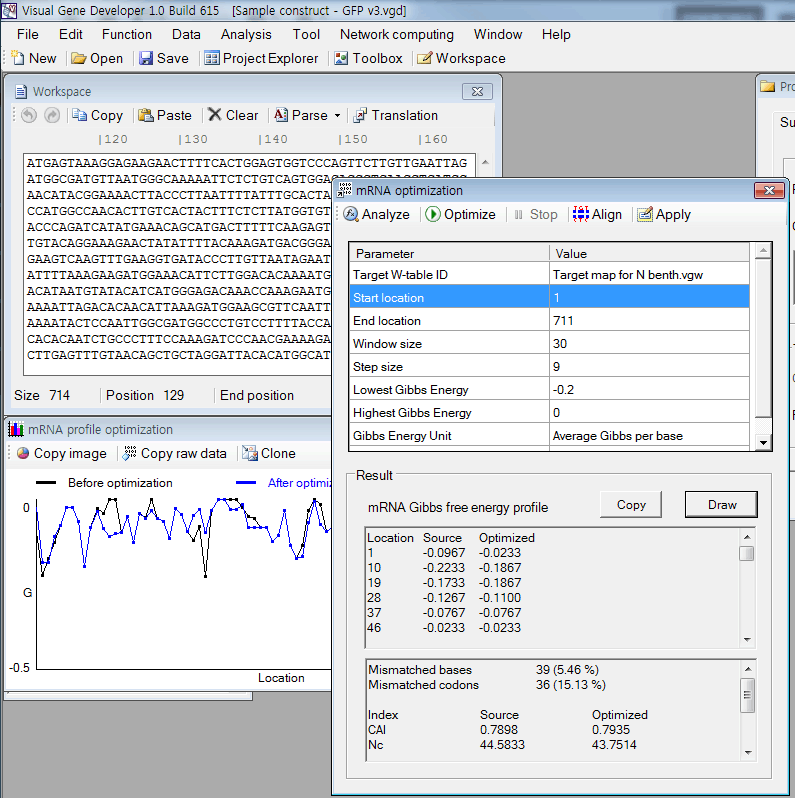
o Simply way to optimize codon on 'mRNA optimization' window
1. Paste any sequence to the 'Workspace' window
2. Click on the menu item (Menu: Function > mRNA optimization)
3. A window titled 'mRNA optimization' will be shown.
4. Click on the 'Perform' button
5. Click on the 'Optimize' button
6. Check results and click on the 'Apply' button.
7. You can check the mRNA profile clicking on the 'Draw' button
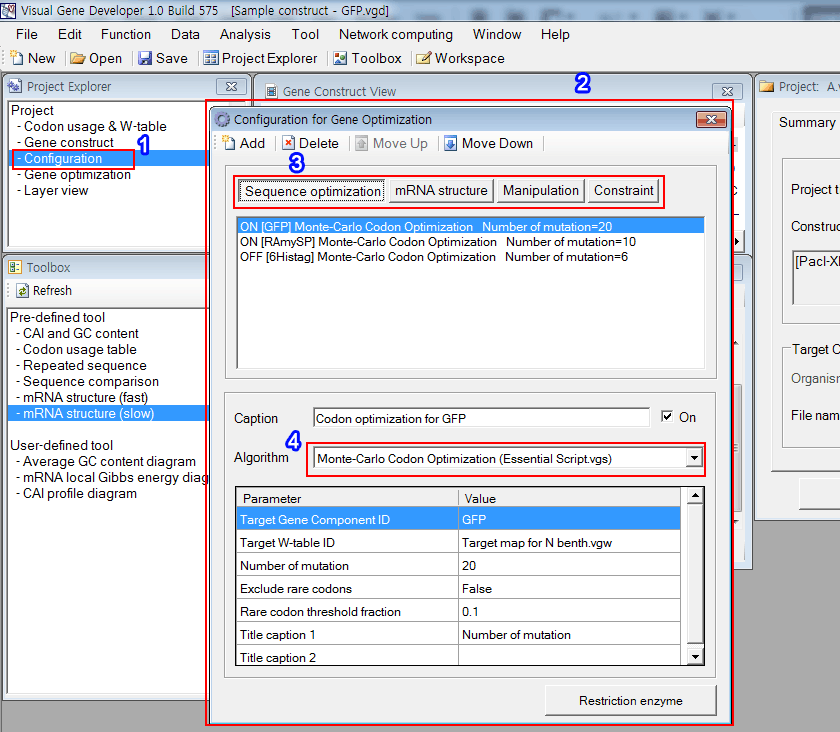
o How to configure optimization condition
1. Click on the 'Configuration' item in the 'Project Explorer' window.
2. A window titled 'Configuration of gene optimization' will be shown.
3. Click on one of the items.
4. Choose one of the algorithms.
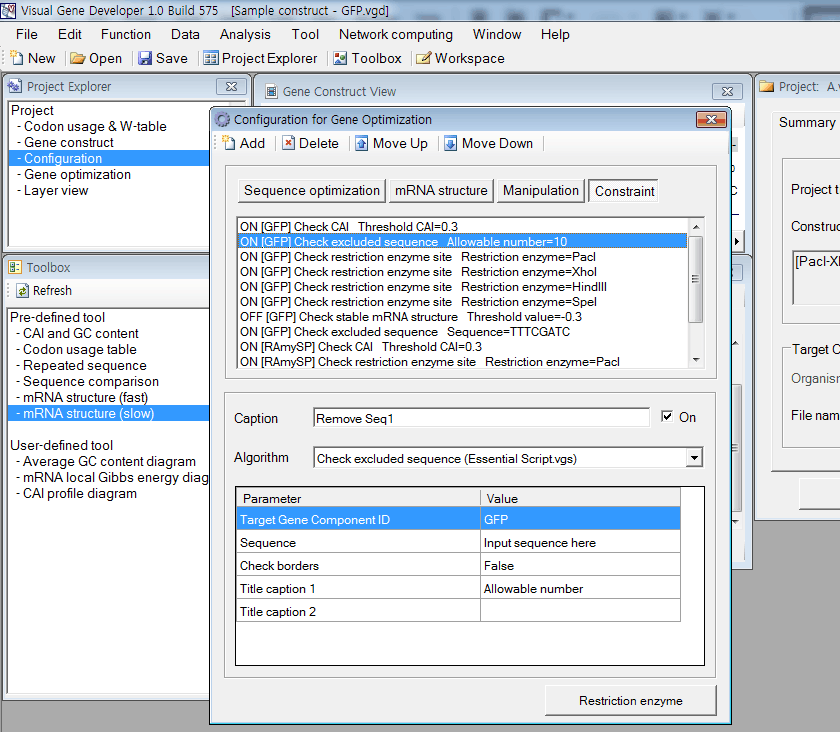
5. In addition, you may click on the 'Constraint'
6. Choose one of the algorithms
7. Adjust parameters. For example, when you click on the 'On' checkbox, it will deactivate a selected module and an optimization algorithm will neglect inactivated items.
o More details about gene optimization procedure
There are 4 different categories of optimization conditions such as 'Sequence optimization', 'mRNA structure', 'Manipulation', and 'Constraint'.
It's up to you to classify the module to one of them. However, internal algorithms orderly proceed from 'Sequence optimization' to 'Constraint'. Therefore, 'Sequence optimization' has the highest priority than other conditions and 'Constraint' is the lowest priority. For more details, check the 'Module development' section on the left menu.
o How to optimize gene construct
1. Click on the 'Configuration' item in the 'Project Explorer' window.
2. A window titled 'Configuration of gene optimization' will be shown. Choose an algorithm and click on the 'Run' button. If you want to stop the optimization, click on the 'Stop' button.
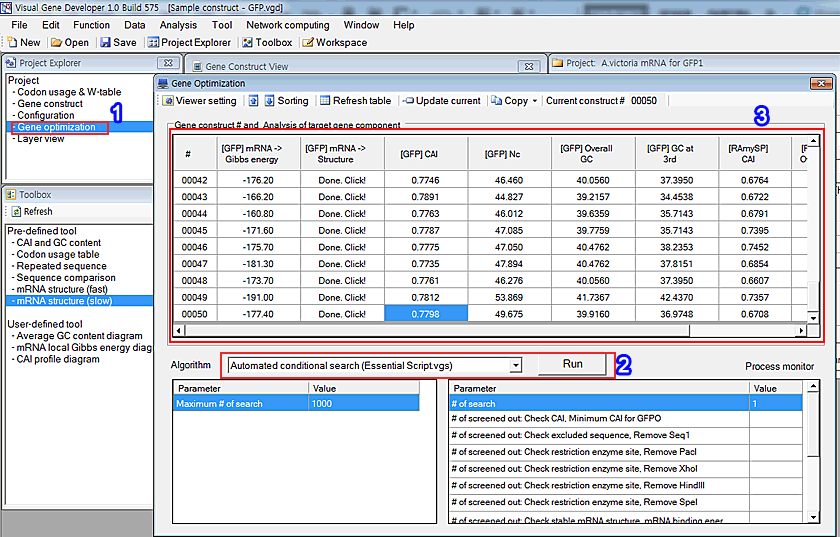
As shown in the figure, the 'Automated conditional search' algorithm produces a lot of candidates that fit for the condition defined in 'Constraint' in the 'Gene optimization condition' window.
3. Because the optimization algorithm initially starts from a selected gene construct (=there are a parent gene construct and lots of child gene constructs), simply choose a gene construct clicking in the table and then start a new optimization cycle.
4. If you want to re-define the table, click on the 'Viewer setting' button in the 'Gene optimization' window.
5. Add/Delete functions in the 'Viewer setting' window.
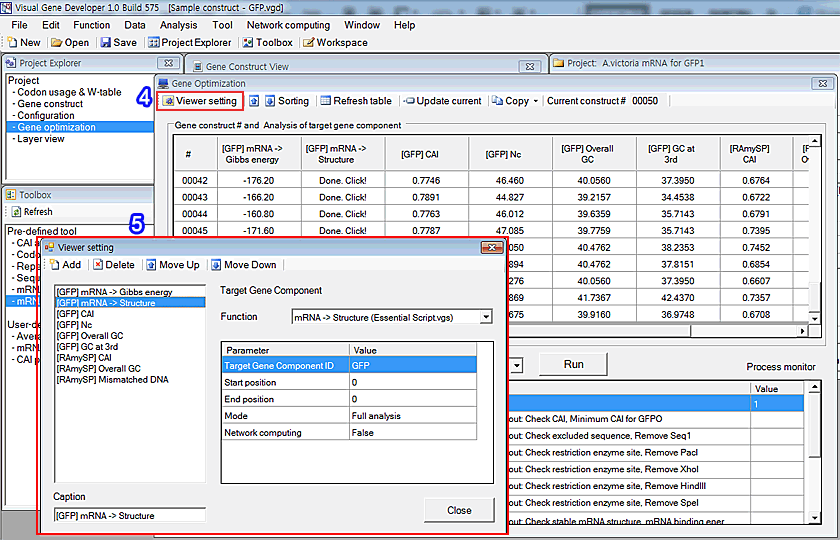
o How to develop a custom gene optimization module?
The software supports developing user-defined new algorithms for gene optimization. The module development section on the left menu will be much helpful. Basically, users can access the gene construct memory array using a class (class name: GeneConstruct) to modify sequence.
Check the following example.
1. Click on the 'Module Library' in the 'Tool' menu
2. Choose 'GeneConstruct.ParameterValue' in the 'Module Library' window
3. Click on the 'Edit Module' button
4. You can see the 'Module Editor' window. Click on the 'Test run' button
5. Check the result and source code.
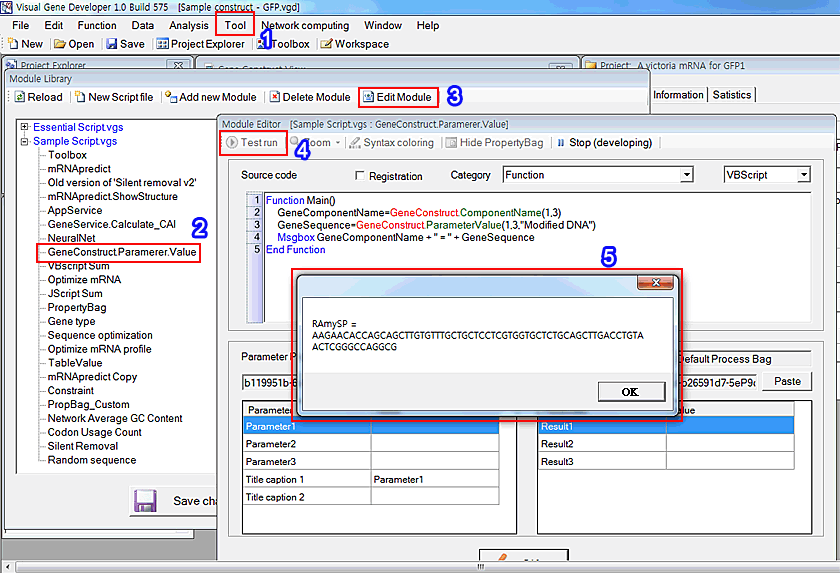
Source code
VBScript
|
Function Main() GeneSequence=GeneConstruct.ParameterValue(1,3,"Modified DNA") '<--- Get parameter value of modified DNA Msgbox GeneComponentName + " = " + GeneSequence '<--- Show result consisting component name and its sequence End Function |
